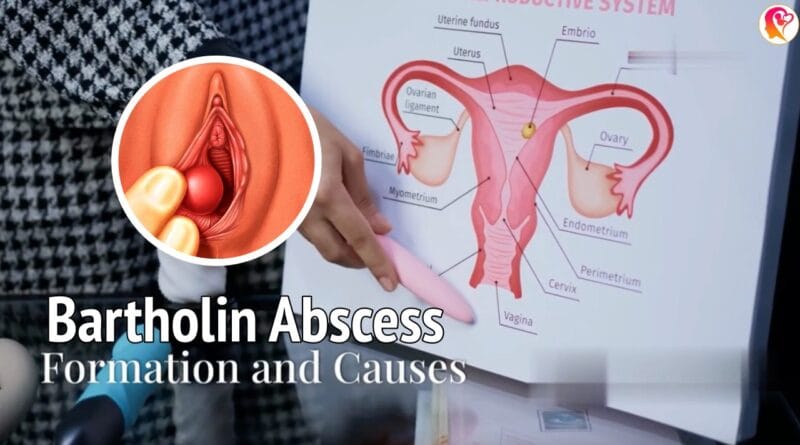
Bartholin Absceses and Cysts: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment 2024
Today’s topic is an important one for many women—Bartholin cysts and abscesses. If you’ve never heard of Bartholin glands before, don’t worry. I’m here to explain what they are, why they might cause problems, and how you can manage them effectively.
What are Bartholin Glands?
Bartholin glands are small, pea-sized glands located on either side of the vaginal opening, inside the labia. Their primary function is to secrete fluid that helps keep the vaginal area lubricated, especially during sexual arousal. These glands release fluid through tiny ducts into the vaginal area to maintain moisture.
What is a Bartholin Cyst?
A Bartholin cyst forms when the ducts of these glands become blocked, preventing the natural flow of fluid. As a result, the fluid builds up, causing a cyst—a fluid-filled sac. Normally, these glands are so small and deep inside the tissue that you wouldn’t feel them, but when they swell due to a blockage, they can become noticeable.
Why Does This Happen?
There are a few reasons why a Bartholin cyst might form:
- Infections: Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as gonorrhea, or other bacterial infections can inflame the gland, causing swelling.
- Duct Blockage: The opening of the gland’s duct might get blocked due to inflammation or trauma, leading to fluid buildup inside the gland.
Symptoms of a Bartholin Cyst
If a Bartholin cyst develops, you may notice swelling, discomfort, or even pain, especially when sitting, walking, or wearing tight clothing. Some women find relief through home remedies, like warm compresses or sitz baths. These methods can help reduce the swelling by improving circulation and promoting drainage.
What is a Bartholin Abscess?
If bacteria, especially from infections, enter the cyst, it can turn into an abscess, which is a collection of pus. Symptoms of an abscess include:
- Increased pain and swelling.
- Fever or chills.
- Difficulty sitting or walking due to severe discomfort.
In these cases, it’s important to see a doctor. Abscesses may require medical intervention, such as drainage or antibiotics to clear the infection.
How to Manage a Bartholin Cyst or Abscess
Now, let’s talk about some common treatment methods:
- Warm Compress or Sitz Bath: A sitz bath involves sitting in warm water mixed with a mild antiseptic, like Betadine, which can help reduce swelling and promote drainage. This is often a first-line home remedy that brings relief.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter painkillers can provide temporary relief from discomfort.
- Medical Treatment: If home remedies don’t help or if the cyst turns into an abscess, visit your doctor. They might prescribe antibiotics or, in some cases, drain the abscess. For recurrent cysts, a minor surgical procedure may be suggested to prevent future blockages.
Preventing Recurrence
Around 20% of women experience recurrent Bartholin cysts. To reduce the chances of this happening:
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Clean your intimate area regularly, especially after using the restroom. Avoid the use of razors in sensitive areas, as small cuts can introduce infections. Opt for safer hair removal methods.
- Avoid Tight Clothing: Wearing loose, breathable fabrics can help minimize friction and irritation.
When to See a Doctor
If you notice persistent swelling, intense pain, or develop a fever, don’t delay seeing a healthcare professional. Timely intervention can prevent complications and ensure a faster recovery.
Conclusion
Bartholin cysts and abscesses are manageable conditions, but staying informed and maintaining proper hygiene are key to preventing and treating them. If you’ve had a Bartholin cyst or abscess before, or if you have any questions, feel free to share in the comments below. And don’t forget to subscribe for more health tips and pregnancy-related content.
Thanks for watching, and take care!”